JSON extension
Usage
The json extension adds support for JSON objects, including a set of functions for JSON
access and manipulation, scanning from, and copying to JSON files. Using this extension, you can
interact with JSON files using LOAD FROM,
COPY FROM, and COPY TO, similar to how you would
with CSV files.
The JSON functionality is not available by default, so you would first need to install the JSON extension by running the following commands:
INSTALL json;LOAD json;See our YouTube video for a walkthrough on how to use the JSON extension:
Example dataset
Let’s look at an example dataset to demonstrate how the JSON extension can be used.
We have 3 JSON files that contain information about patients and their medical conditions. The
files are organized into two node files (patient.json and condition.json) and one relationship
file (has_condition.json).
[ { "p_id": "p1", "name": "Gregory", "info": { "height": 1.81, "weight": 75.5, "age": 35, "insurance_provider": [ { "type": "health", "name": "Blue Cross Blue Shield", "policy_number": "1536425345" }, { "type": "dental", "name": "Cigna dental", "policy_number": "745332412" } ] } }, { "p_id": "p2", "name": "Alicia", "info": { "height": 1.65, "weight": 60.1, "age": 28, "insurance_provider": [ { "type": "health", "name": "Aetna", "policy_number": "9876543210" } ] } }, { "p_id": "p3", "name": "Rebecca" }][ { "c_id": "c1", "name": "Diabetes (Type 1)", "description": "Diabetes is a chronic condition where the body can't properly regulate blood sugar levels, either due to insufficient insulin production or ineffective use of insulin, leading to potential health complications." }, { "c_id": "c2", "name": "Asthma", "description": "Asthma is a chronic condition that affects the airways in your lungs, causing inflammation and narrowing of the airways. This can lead to difficulty breathing, coughing, and other symptoms." }, { "c_id": "c3", "name": "Allergic Rhinitis", "description": "Allergic rhinitis, also known as hay fever, is a condition where your immune system overreacts to allergens like pollen, mold, or pet dander, causing symptoms like sneezing, congestion, and nasal itching." }, { "c_id": "c4", "name": "Migraine", "description": "Migraine is a common neurological condition characterized by recurring headaches with associated symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light or sound. It can be severe and disabling, impacting daily life." }][ { "from": "p1", "to": "c1", "since": 2019 }, { "from": "p1", "to": "c2", "since": 2015 }, { "from": "p2", "to": "c1", "since": 2022 }, { "from": "p2", "to": "c4", "since": 2020 }]In the following sections, we will first scan the JSON files to query its contents in Cypher, and then proceed to copy the JSON data and construct a graph.
Scan the JSON file
LOAD FROM is a Cypher query that scans a file or object element by element, but doesn’t actually
move the data into a Kuzu table.
Because the JSON format contains simple data types without type information, the structure will be inferred.
To declare type information explicitly, you can use LOAD WITH HEADERS like you would for CSV files.
To scan the file above, you can do the following:
LOAD FROM 'patient.json' RETURN *;┌────────┬─────────┬──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ p_id │ name │ info ││ STRING │ STRING │ STRUCT(height DOUBLE, weight DOUBLE, age UINT8, insurance_provider STRUCT(type STRING, name STRING, policy_number STRING)[]) │├────────┼─────────┼──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤│ p1 │ Gregory │ {height: 1.810000, weight: 75.500000, age: 35, insurance_provider: [{type: health, name: Blue Cross Blue Shield, policy_number: 1536425345},{type: dental, name: Cigna dental, policy_number: 7453324... ││ p2 │ Alicia │ {height: 1.650000, weight: 60.100000, age: 28, insurance_provider: [{type: health, name: Aetna, policy_number: 9876543210},{type: vision, name: VSP, policy_number: 1784567890}]} ││ p3 │ Rebecca │ {height: 1.780000, weight: , age: 23, insurance_provider: [{type: health, name: Blue Cross Blue Shield, policy_number: 5678901234}]} │└────────┴─────────┴──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Because info is a nested object, its type in Kuzu is inferred as a STRUCT, that itself contains
other types, like DOUBLE, UINT8, STRING, and STRUCT.
Missing keys
Missing keys, i.e., keys that are present in one JSON blob but not in another, are returned as the default/empty value for the type. To test this, let’s run another query to get the name, age, height, weight and insurance provider of all patients:
LOAD FROM 'patient.json' RETURN name, info.age, info.height, info.weight, info.insurance_provider;┌─────────┬──────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ name │ STRUCT_EXTRACT(info,age) │ STRUCT_EXTRACT(info,height) │ STRUCT_EXTRACT(info,weight) │ STRUCT_EXTRACT(info,insurance_provider) ││ STRING │ UINT8 │ DOUBLE │ DOUBLE │ STRUCT(type STRING, name STRING, policy_number STRING)[] │├─────────┼──────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤│ Gregory │ 35 │ 1.810000 │ 75.500000 │ [{type: health, name: Blue Cross Blue Shield, policy_number:... ││ Alicia │ 28 │ 1.650000 │ 60.100000 │ [{type: health, name: Aetna, policy_number: 9876543210}] ││ Rebecca │ 0 │ 0.000000 │ 0.000000 │ [] │└─────────┴──────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘As can be seen, the patient Rebecca is new in the system and is missing her information fields:
ageis set to the default value of0forUINT8heightandweightare set to the default value of0.0forDOUBLEinsurance_provideris set to an empty array[]
Enforcing types
To enforce the data type during scanning, use the LOAD WITH HEADERS feature.
Example:
LOAD WITH HEADERS ( p_id STRING, name STRING, info STRUCT( height FLOAT, weight FLOAT, age UINT8, insurance_provider STRUCT(type STRING, name STRING, policy_number STRING)[] ))FROM 'patient.json'RETURN name, info.height, info.weight;We can see that the types inside the info STRUCT are now enforced to FLOAT, rather than DOUBLE.
┌─────────┬─────────────────────────────┬─────────────────────────────┐│ name │ STRUCT_EXTRACT(info,height) │ STRUCT_EXTRACT(info,weight) ││ STRING │ FLOAT │ FLOAT │├─────────┼─────────────────────────────┼─────────────────────────────┤│ Gregory │ 1.810000 │ 75.500000 ││ Alicia │ 1.650000 │ 60.099998 ││ Rebecca │ 0.000000 │ 0.000000 │└─────────┴─────────────────────────────┴─────────────────────────────┘Optional parameters
The following optional parameters are supported:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
maximum_depth | Default value is 10. Used by the type inference system to determine how “deep” into the json document to go to infer types. |
sample_size | Default value 2048. Used by the type inference system to determine the number of elements used to infer the json type. |
Copy JSON files to a table
The COPY FROM statement allows you to copy data from a JSON file into a node or relationship table in Kuzu.
In this section we will walk through the example dataset shown above and build a graph from the JSON data.
Copy to node tables
First, start by defining a node table schema that conforms to the JSON structure. For nested fields,
we declare a STRUCT where necessary.
Example:
CREATE NODE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Patient( p_id STRING, name STRING, info STRUCT( height FLOAT, weight FLOAT, age UINT8, insurance_provider STRUCT( type STRING, name STRING, policy_number STRING )[] ), PRIMARY KEY (p_id))The syntax STRUCT( ... )[] with the square braces at the end represents an arrya of STRUCTs.
You can then use a COPY FROM statement to directly copy the contents of the JSON file into the
node table.
COPY Patient FROM 'patient.json'Similarly, we can define the node table for the patients’ medical conditions.
CREATE NODE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS Condition( c_id STRING, name STRING, description STRING, PRIMARY KEY (c_id))And copy the contents of condition.json to the node table as follows:
conn.execute("COPY Condition FROM 'condition.json'")Copy to relationship tables
To copy from a JSON file to a relationship table, the file must contain the "from" and "to" keys.
In the example dataset for has_condition.json, we have these keys defined:
[ { "from": "p1", "to": "c1", "since": 2019 }, { "from": "p1", "to": "c2", "since": 2015 }, ...]Any other keys that are not "from" or "to" are treated as relationship properties.
Let’s create a relationship table schema:
CREATE REL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS HAS_CONDITION( FROM Patient TO Condition, since UINT16)The has_condition.json file can then directly be copied into the relationship table that was just created.
COPY HAS_CONDITION FROM 'has_condition.json'We obtain the following graph:
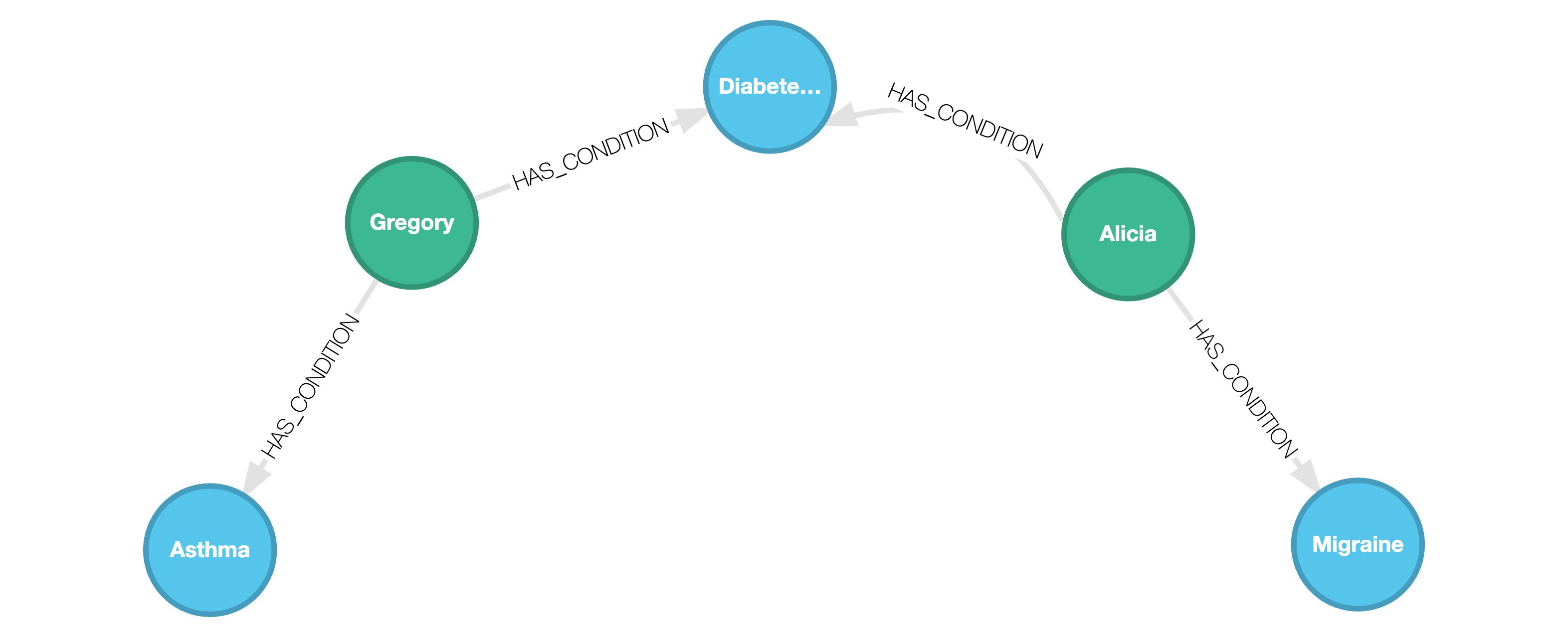
Any nested fields are ingested into the graph as STRUCTs. We can query on these nested fields as shown below:
MATCH (p:Patient)-[:HAS_CONDITION]->(c:Condition)WHERE c.name = "Diabetes (Type 1)"WITH p.name AS name, p.info.age AS age, c.name AS condition, p.info.insurance_provider AS ipUNWIND ip AS providerWITH name, age, provider, conditionWHERE provider.type = "health"RETURN name, age, condition, provider.name AS health_insurance_provider┌─────────┬───────┬───────────────────┬───────────────────────────┐│ name │ age │ condition │ health_insurance_provider ││ STRING │ UINT8 │ STRING │ STRING │├─────────┼───────┼───────────────────┼───────────────────────────┤│ Gregory │ 35 │ Diabetes (Type 1) │ Blue Cross Blue Shield ││ Alicia │ 28 │ Diabetes (Type 1) │ Aetna │└─────────┴───────┴───────────────────┴───────────────────────────┘Note how the UNWIND clause was used to obtain individual records of the insurance providers for
each patient.
UNWIND JSON arrays
In the above example, we have useful information about insurance providers that could also be used to capture the relationships between patients and their insurance providers.
Let’s model this using a new node table, InsuranceProvider, and a new relationship table HAS_PROVIDER.
CREATE NODE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS InsuranceProvider( name STRING, type STRING, PRIMARY KEY (name))
CREATE REL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS HAS_PROVIDER( FROM Patient TO InsuranceProvider, policy_number STRING)We can then UNWIND the insurance providers for each patient, obtain distinct providers, and then
pass these results via a subquery to COPY FROM.
COPY InsuranceProvider FROM ( LOAD FROM 'patient.json' WITH info.insurance_provider AS ip UNWIND ip AS provider RETURN DISTINCT provider.name AS name, provider.type AS type)Let’s break down the above query step by step:
- The outer
COPY FROMexpects the result from the innerLOAD FROM - The info
STRUCTfrompatient.jsonis passed toUNWINDso that we can obtain individual providers for each patient - A
DISTINCTclause is used when returning the results of the subquery, because thenameof a provider is the primary key of theInsuranceProvidernode table per the schema created above (we cannot have duplicate values for primary keys).
We can do a similar sequence of steps to copy relationships from patient.json as follows:
COPY HAS_PROVIDER FROM ( LOAD FROM 'patient.json' WITH p_id, info.insurance_provider AS ip UNWIND ip AS provider RETURN p_id, provider.name AS name, provider.policy_number AS policy_number)In this case, we didn’t alias the first two entries to from and to, like we did when copying
from the has_condition.json file above. This is because the COPY FROM query is looking for the
first two columns in the result as the FROM and the TO columns in the relationship, similar to
how it’s done in CSV.
We now obtain the following graph:
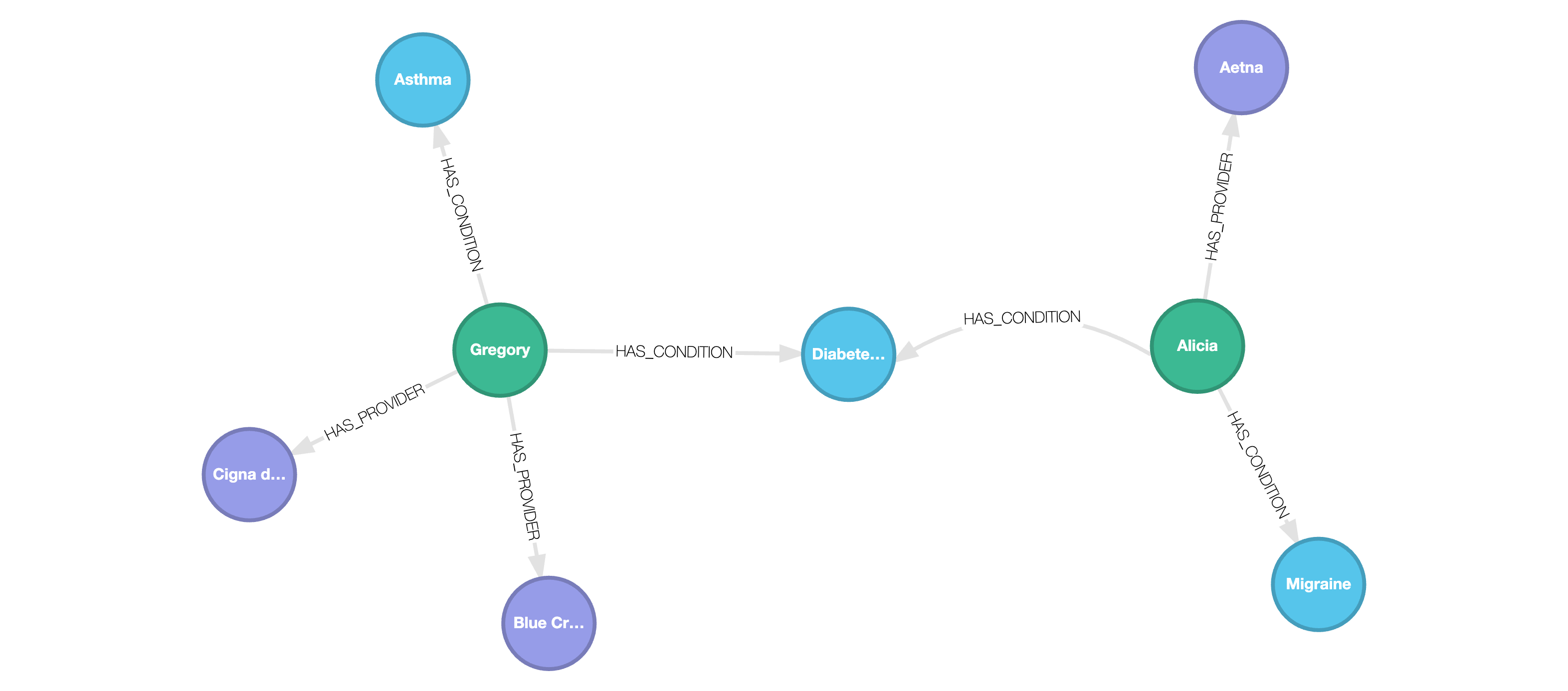
Copy query results to JSON files
Once you have the data in a graph, you can begin querying it in Cypher. You can use the COPY TO
statement to write the results of a query to a JSON file. Any query results of the type STRUCT
will be written as nested JSON. Two examples are shown below.
Say you want to write health insurance provider information and patient names for patients with the
condition “Migraine” to a JSON file named patient_providers.json.
COPY ( MATCH (p:Patient)-[:HAS_CONDITION]->(c:Condition) WHERE c.name = "Migraine" WITH p.name AS name, p.info.age AS age, c.name AS condition, p.info.insurance_provider AS ip UNWIND ip AS provider WITH name, age, provider, condition WHERE provider.type = "health" RETURN name, age, condition, provider) TO 'patient_providers.json';The output JSON would look like this:
[ { "name": "Alicia", "age": 28, "condition": "Migraine", "provider": { "type": "health", "name": "Aetna", "policy_number": "9876543210" } }]Say we want to write the name of the condition and a list of patient names who have the condition
and have health insurance to a JSON file named patients_with_condition.json. This is how we
would query the graph:
COPY ( MATCH (c:Condition)<-[:HAS_CONDITION]-(a:Patient)-[:HAS_PROVIDER]->(pr:InsuranceProvider) WHERE c.name = 'Diabetes (Type 1)' AND pr.type = 'health' RETURN c.name AS condition, COLLECT(a.name) AS patients;) TO 'patients_with_condition.json';The output JSON would look like this:
[ { "condition": "Diabetes (Type 1)", "patients": [ "Gregory", "Alicia" ] }]Takeaways
When using the JSON extension, keep in mind the following considerations when copying data to Kuzu tables:
-
The order of the keys in the JSON file doesn’t need to match with the order of the columns defined in the schema (just the names need to match)
-
If directly copying from a JSON file to a relationship table, there need to be keys named
"from"and"to"in the file, whose values point to the primary key values of the underlying node tables. -
You can combine
LOAD FROMsubqueries withCOPY FROMto have more control over the subset of JSON data being copied, as well as dynamically transform your data viaUNWINDorDISTINCTclauses, so it’s not necessary to write your relationships to an intermediate file prior to usingCOPY.
JSON data type
Using the Kuzu JSON extension, you can model and store properties as JSON natively via the JSON logical type,
which is interpreted as parsed as JSON, rather than as a string.
The following example creates a node table Person with a JSON column description,
it then creates two json objects in this column using to_json function, and outputs them.
Example:
INSTALL json;LOAD json;
CREATE NODE TABLE Person (id INT64, description JSON, primary key(id));CREATE (p:Person {id: 20, description: to_json({height: 52, age: 32, scores: [1,2,5]})});CREATE (p:Person {id: 40, description: to_json({age: 55, scores: [1,32,5,null], name: 'dan'})});MATCH (p:Person) RETURN p.*;Result:
┌───────┬────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ p.id │ p.description ││ INT64 │ json │├───────┼────────────────────────────────────────────────┤│ 20 │ {"height":52,"age":32,"scores":[1,2,5]} ││ 40 │ {"age":55,"scores":[1,32,5,null],"name":"dan"} │└───────┴────────────────────────────────────────────────┘You can then query on these properties as follows:
MATCH (p:Person)WHERE json_extract(p.description, 'age') < 50RETURN p.id AS id, json_extract(p.description, 'age') AS age;Result:
┌───────┬──────┐│ id │ age ││ INT64 │ json │├───────┼──────┤│ 20 │ 32 │└───────┴──────┘JSON functions
This section lists the built-in functions that operate on the JSON data type within Kuzu.
to_json
Signature: ANY -> JSON
to_json(any)
Converts any Kuzu value to JSON.
Example 1:
RETURN to_json('{"name": "Gregory"}') AS person;┌────────────────────┐│ person ││ json │├────────────────────┤│ {"name":"Gregory"} │└────────────────────┘Example 2:
RETURN to_json([1,2,3]) AS json_array;┌────────────┐│ json_array ││ json │├────────────┤│ [1,2,3] │└────────────┘Example 3:
RETURN to_json('Alicia') AS simple_string;┌───────────────┐│ simple_string ││ json │├───────────────┤│ "Alicia" │└───────────────┘array_to_json
Signature: ARRAY -> JSON
Alias for to_json that only accepts ARRAY.
row_to_json
Signature: LIST -> JSON
Alias for to_json that only accepts LIST.
cast(ANY AS JSON)
Signature: ANY -> JSON
Syntax sugar for to_json(any) -> JSON,
cast can cast ANY type to be some type other than JSON as well,
Read the instruction of Casting for more details.
Example:
RETURN cast('{"name": "Alicia", "age": 28}' AS JSON);┌───────────────────────────────────────────┐│ CAST({"name": "Alicia", "age": 28}, json) ││ json │├───────────────────────────────────────────┤│ {"name":"Alicia","age":28} │└───────────────────────────────────────────┘json_object
Signature: STRING, ANY -> JSON object
json_object([key, value, ...])
Create a JSON object from any number of key, value pairs.
Example 1:
RETURN json_object("name", "Alicia");┌──────────────────────────┐│ json_object(name,Alicia) ││ json │├──────────────────────────┤│ {"name":"Alicia"} │└──────────────────────────┘Example 2:
RETURN json_object("name", "Alicia", "age", 28);┌─────────────────────────────────┐│ json_object(name,Alicia,age,28) ││ json │├─────────────────────────────────┤│ {"name":"Alicia","age":28} │└─────────────────────────────────┘json_array
Signature: ARRAY -> JSON ARRAY
json_array([any, ...])
Create an array of JSON objects from any number of values. Each value is converted into a JSON object.
Example:
RETURN json_array("Alicia", "25", NULL);┌────────────────────────┐│ json_array(Alicia,25,) ││ json │├────────────────────────┤│ ["Alicia","25",null] │└────────────────────────┘json_merge_patch
Signature: JSON, JSON -> JSON
json_merge_patch(json, json)
Merges TWO JSON documents. Applies RFC 7386
Example 1:
RETURN json_merge_patch('{"name": "Alicia"}', '{"age": 28}');┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────┐│ json_merge_patch({"name": "Alicia"},{"age": 28}) ││ json │├──────────────────────────────────────────────────┤│ {"name":"Alicia","age":28} │└──────────────────────────────────────────────────┘Example 2:
Merging with a NULL path would result in NULL path.
RETURN json_merge_patch("3", NULL);┌──────────────────────┐│ json_merge_patch(3,) ││ json │├──────────────────────┤│ │└──────────────────────┘json_extract
Signatures: JSON, STRING -> JSON, JSON, INTEGER -> JSON, JSON, LIST -> LIST of JSON
json_extract(json, path)
Extracts JSON from json at the given path.
path is a STRING delimited by '/'.
Integers may also be used to represent the path, which represents the index if the input is a JSON array.
If path is a LIST of paths, the result will also be a LIST.
If the path does not exist, this function returns an empty JSON document.
Examples:
In this case, we provide a single item as the path.
RETURN json_extract('{"Software": {"Database": ["duck", "kuzu"]}}', 'Software/Database/1') AS extracted;┌───────────┐│ extracted ││ json │├───────────┤│ "kuzu" │└───────────┘Here, we provide a LIST of paths:
RETURN json_extract('{"Software": {"Database": ["duck", "kuzu"]}}', ['Software/Database/1', 'Software/Database/0']) AS extracted;┌─────────────────┐│ extracted ││ json[] │├─────────────────┤│ ["kuzu","duck"] │└─────────────────┘This example provides the path as an integer that represents the index of the item in the JSON array we want to extract:
RETURN json_extract('[1, 2, 42]', 2) AS nums;┌──────┐│ nums ││ json │├──────┤│ 42 │└──────┘Extracting from an empty path results in empty JSON document:
RETURN json_extract('{"Software": {"Database": ["duck", "kuzu"]}}', "") AS extracted;┌───────────┐│ extracted ││ json │├───────────┤│ │└───────────┘json_array_length
Signature: JSON -> UINT32
json_array_length(json[])
If the json is an JSON array, return its length. Otherwise return 0.
Example 1:
RETURN json_array_length('["1", "1", "4", null]') AS len;┌────────┐│ len ││ UINT32 │├────────┤│ 4 │└────────┘Example 2:
Trying to compute the length of a JSON array with a null value results in a length of zero, as
this isn’t valid JSON array.
RETURN json_array_length('{"kuzu": ["1", "1", "4", null]}') AS len;┌────────┐│ len ││ UINT32 │├────────┤│ 0 │└────────┘json_contains
Signature: JSON, JSON -> BOOL
json_contains(json_haystack, json_needle)
Returns True if json_needle is contained in json_haystack. Both parameters are of JSON type, but json_needle can also be a numeric value or a string, however the string must be wrapped in double quotes.
Example 1:
RETURN JSON_CONTAINS('{"name": "Alicia"}', '"Alicia"') AS found_name;┌────────────┐│ found_name ││ BOOL │├────────────┤│ True │└────────────┘Example 2:
RETURN JSON_CONTAINS('{"age": 28}', '28') AS found_age;┌───────────┐│ found_age ││ BOOL │├───────────┤│ True │└───────────┘json_keys
Signature: JSON -> STRING[]
json_keys(json)
Return keys of the root json object. If the root is not an JSON object, return an empty list.
Examples:
RETURN json_keys('{ "family": "anatidae", "species": [ "duck", "goose", "swan", null ] }') AS keys;┌──────────────────┐│ keys ││ STRING[] │├──────────────────┤│ [family,species] │└──────────────────┘json_structure
Signature: JSON -> STRING
json_structure(json)
Returns the structure of the json in Kuzu type notation. Integer widths are automatically inferred from input values.
Example:
RETURN json_structure('[{"a": -1, "b": [1000, 2000, 3000]}, {"a": 2, "c": "hi"}]') AS structure;┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐│ structure ││ STRING │├─────────────────────────────────────────┤│ STRUCT(a INT16, b UINT16[], c STRING)[] │└─────────────────────────────────────────┘json_valid
Signature: JSON -> BOOL
json_valid(json)
Determines whether or not the provided json is valid JSON.
Example 1:
RETURN json_valid('{"name": "Alicia", "age": 28}') AS is_valid;┌──────────┐│ is_valid ││ BOOL │├──────────┤│ True │└──────────┘Example 2:
RETURN json_valid('"name": "Alicia", "age": 28') AS is_valid;┌──────────┐│ is_valid ││ BOOL │├──────────┤│ False │└──────────┘json
Signature: JSON -> JSON
json(json)
Parses and minifies the JSON.
Example:
UNWIND ['[ {"a": [1], "b": 2,"c": 1}, 1, 5, 9]', '[1, 2, 3]', '"ab"'] AS ARR RETURN json(ARR);┌───────────────────────────────┐│ json(ARR) ││ json │├───────────────────────────────┤│ [{"a":[1],"b":2,"c":1},1,5,9] ││ [1,2,3] ││ "ab" │└───────────────────────────────┘
