Query and visualize your graph
Cypher is a declarative query language for graphs, and should be easy to get started with for anyone who is familiar with SQL. Kuzu’s implementation of Cypher is based on the openCypher standard.
This section will briefly cover how to use Cypher to query the graph created in the previous section. For a detailed guide on using Cypher in Kuzu and to see all the available functions, see the Cypher manual.
Query interfaces
There are three ways you can query an existing Kuzu database:
- CLI: Write Cypher queries directly in the Kuzu CLI shell.
- Kuzu Explorer: Interactively write and run Cypher queries using Kuzu Explorer, a web-based query interface that also provides graph visualization.
- Client APIs: Integrate Kuzu in your application using your preferred programming language.
Cypher introduction
For simplicity, we’ll demonstrate how to run Cypher queries using Kuzu Explorer. You are welcome to run the same queries via the CLI or your preferred client language APIs.
The advantage of using Kuzu Explorer to run queries during the prototyping and exploration phase is that you can visualize the graph as you query it. Additionally, you can view the query results as a table or as JSON, allowing you to easily design and test your application logic.
Open a database in Kuzu Explorer
Run the appropriate version of Kuzu Explorer via Docker as follows:
docker run --rm -p 8000:8000 \ -v /path/to/example.kuzu:/database \ kuzudb/explorer:latest
docker run -p 8000:8000 \ -v /path/to/local/directory:/database \ -e KUZU_FILE=example.kuzu \ --rm kuzudb/explorer:latestVisualize nodes and relationships
Our first Cypher query will use the MATCH statement to display all nodes and relationships from all tables:
MATCH (a)-[b]->(c)RETURN *;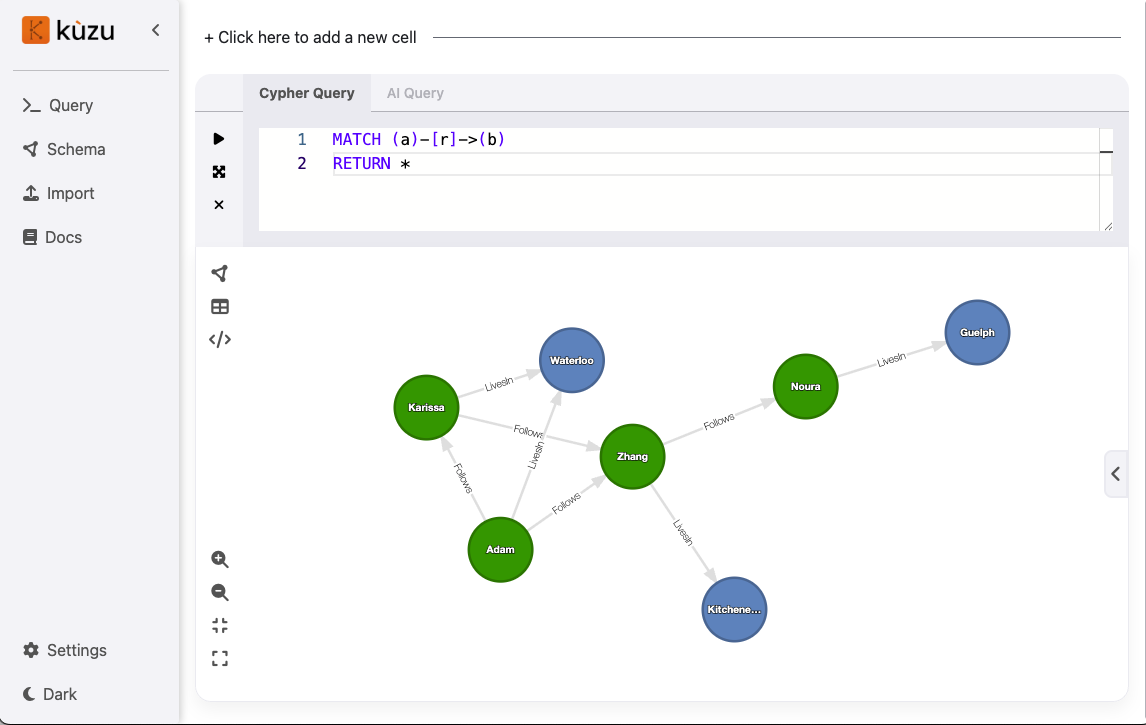
Note that this is a sample graph with only a small number of nodes and relationships. For real-world
graphs, you will likely want to limit the number of returned nodes and relationships by using the LIMIT clause.
MATCH (a)-[b]->(c)RETURN *LIMIT 10;Match nodes by label
You can match on a particular node label using its table name as shown below:
MATCH (a:User)RETURN a.name AS name, a.age AS age;┌─────────┬───────┐│ name │ age ││ STRING │ INT64 │├─────────┼───────┤│ Adam │ 30 ││ Karissa │ 40 ││ Zhang │ 50 ││ Noura │ 25 │└─────────┴───────┘Note how the name and age properties are aliased in the RETURN statement.
Match relationships by label
Similarly, you can match on a particular relationship label using its table name as shown below:
MATCH (a)-[e:Follows]->(b)RETURN a.name AS user1, b.name AS user2, e.since AS follows_since;┌─────────┬─────────┬───────────────┐│ user1 │ user2 │ follows_since ││ STRING │ STRING │ INT64 │├─────────┼─────────┼───────────────┤│ Adam │ Karissa │ 2020 ││ Adam │ Zhang │ 2020 ││ Karissa │ Zhang │ 2021 ││ Zhang │ Noura │ 2022 │└─────────┴─────────┴───────────────┘Equality predicates on node/relationship properties
MATCH (a:User)-[e:Follows {since: 2020}]->(b:User {name: "Karissa"})RETURN b.name AS user, a.name AS follower, e.since AS follows_since;┌─────────┬──────────┬───────────────┐│ user │ follower │ follows_since ││ STRING │ STRING │ INT64 │├─────────┼──────────┼───────────────┤│ Karissa │ Adam │ 2020 │└─────────┴──────────┴───────────────┘Note that the predicates on properties are enclosed in curly braces {}. This is functionally equivalent
to using a WHERE clause in Cypher. The following query would return the same result:
MATCH (a:User)-[e:Follows]->(b:User)WHERE e.since = 2020 AND b.name = "Karissa"RETURN b.name AS user, a.name AS follower, e.since AS follows_since;Cypher tutorial
For a more detailed introduction to Cypher, read the Cypher tutorial.

