Run graph algorithms
One of the overarching goals of Kuzu is to function as the go-to graph database for data science use cases.
Using the algo extension
The official algo Kuzu extension allows you to run graph algorithms directly
inside Kuzu using Cypher queries. We currently support some common graph algorithms, including
PageRank, Connected Components, and Louvain, and plan to grow the set of supported algorithms in
the future.
Refer to the documentation for more details on how to install and use the extension.
Using NetworkX
NetworkX is a popular library in Python for graph algorithms and data science. In this
section, we demonstrate Kuzu’s ease of use in exporting subgraphs to the NetworkX format using the
get_as_networkx() function in the Python API. We also demonstrate the following capabilities:
- Graph Visualization: We visualize subgraphs of interest via Kuzu Explorer.
- PageRank: We compute PageRank on an extracted subgraph, store these values back in Kuzu’s node tables, and query them using Cypher.
We will use the MovieLens dataset.
The linked dataset represents a smaller subset extracted from the original source and contains
610 User nodes, 9724 Movie nodes, 100,863 Rating edges, and 3684 Tags edges. The schema of the
dataset is shown below.

mkdir ./movie_data/curl -L -o ./movie_data/movies.csv https://kuzudb.com/data/movie-lens/movies.csvcurl -L -o ./movie_data/users.csv https://kuzudb.com/data/movie-lens/users.csvcurl -L -o ./movie_data/ratings.csv https://kuzudb.com/data/movie-lens/ratings.csvcurl -L -o ./movie_data/tags.csv https://kuzudb.com/data/movie-lens/tags.csvImport data into Kuzu
Import the data into a Kuzu database using the Python API:
import kuzu
def copy_data(connection): connection.execute('CREATE NODE TABLE Movie (movieId INT64 PRIMARY KEY, year INT64, title STRING, genres STRING);') connection.execute('CREATE NODE TABLE User (userId INT64 PRIMARY KEY);') connection.execute('CREATE REL TABLE Rating (FROM User TO Movie, rating DOUBLE, timestamp INT64);') connection.execute('CREATE REL TABLE Tags (FROM User TO Movie, tag STRING, timestamp INT64);')
connection.execute('COPY Movie FROM "./movies.csv" (HEADER=TRUE);') connection.execute('COPY User FROM "./users.csv" (HEADER=TRUE);') connection.execute('COPY Rating FROM "./ratings.csv" (HEADER=TRUE);') connection.execute('COPY Tags FROM "./tags.csv" (HEADER=TRUE);')
db = kuzu.Database("ml_small.kuzu")conn = kuzu.Connection(db)copy_data(conn)Visualize subgraphs in Kuzu Explorer
You can visualize the imported data in Kuzu Explorer as shown in the previous section:
// Return the first two users, their movies, and their ratingsMATCH (u:User)-[r:Rating]->(m:Movie)WHERE u.userId IN [1, 2]RETURN u, r, mLIMIT 100;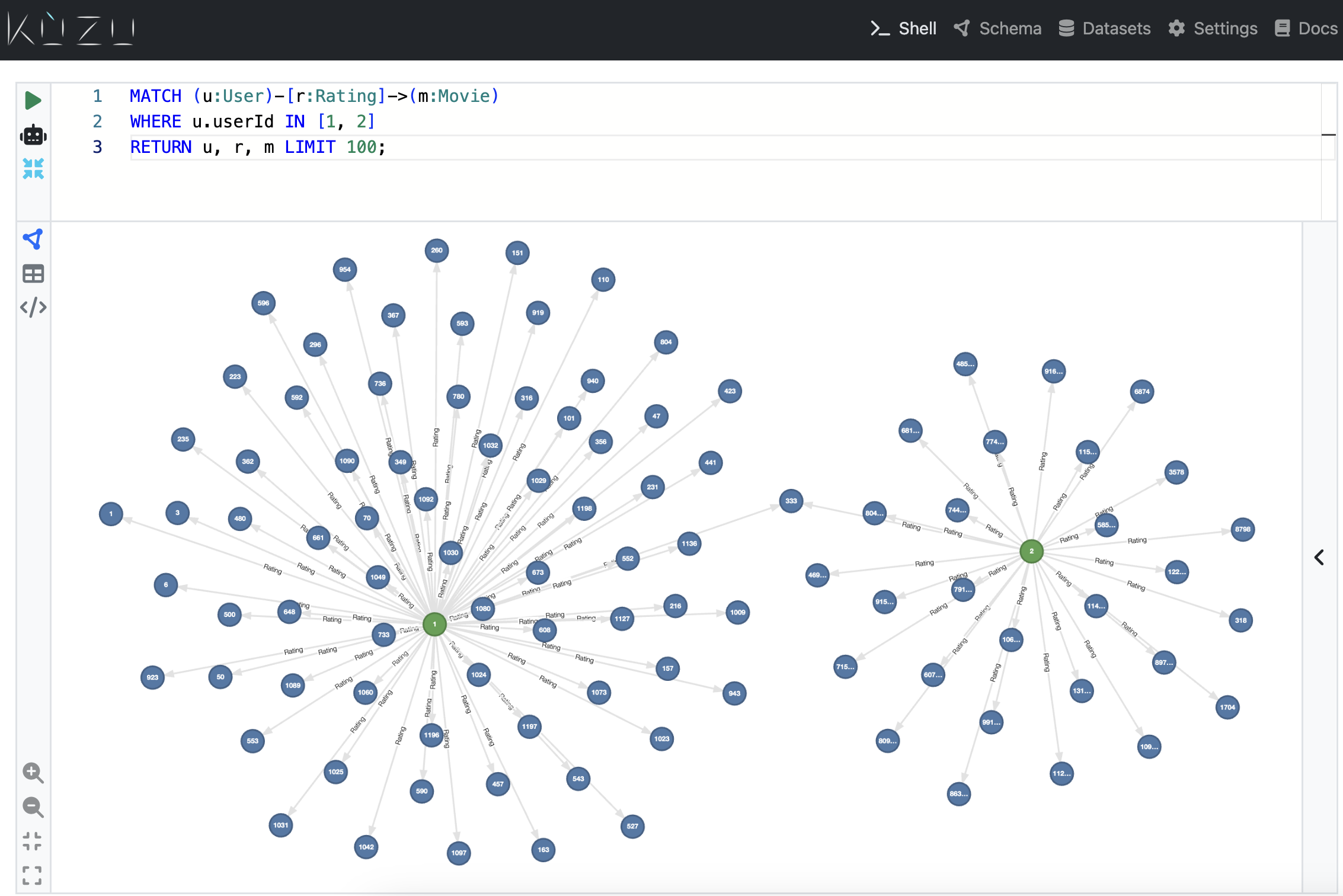
Export subgraph to NetworkX
You can extract a subgraph of the edges between User and Movie nodes (ignoring Tags edges)
and convert it to a NetworkX graph G.
# pip install networkxres = conn.execute('MATCH (u:User)-[r:Rating]->(m:Movie) RETURN u, r, m;')G = res.get_as_networkx(directed=False)We store the extracted subgraph as an undirected graph in NetworkX because the direction doesn’t matter for the PageRank algorithm.
Compute PageRank
Compute the PageRank of the subgraph G using NetworkX’s pagerank function.
import networkx as nx
pageranks = nx.pagerank(G)The PageRank values for the Movie nodes can then be exported into a Pandas DataFrame:
import pandas as pd
pagerank_df = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(pageranks, orient="index", columns=["pagerank"])movie_df = pagerank_df[pagerank_df.index.str.contains("Movie")]movie_df.index = movie_df.index.str.replace("Movie_", "").astype(int)movie_df = movie_df.reset_index(names=["id"])print(f"Calculated pageranks for {len(movie_df)} nodes\n")print(movie_df.sort_values(by="pagerank", ascending=False).head())Calculated pageranks for 9724 nodes
id pagerank20 356 0.001155232 318 0.00109916 296 0.001075166 2571 0.00100634 593 0.000987Similarly, we can store the PageRank values for the User nodes in a Pandas DataFrame:
user_df = pagerank_df[pagerank_df.index.str.contains("User")]user_df.index = user_df.index.str.replace("User_", "").astype(int)user_df = user_df.reset_index(names=["id"])user_df.sort_values(by="pagerank", ascending=False).head()Write PageRank values back to Kuzu
To write the values back to Kuzu, first update the node table schemas to include a new property
pagerank.
try: # Alter original node table schemas to add pageranks conn.execute("ALTER TABLE Movie ADD pagerank DOUBLE DEFAULT 0.0;") conn.execute("ALTER TABLE User ADD pagerank DOUBLE DEFAULT 0.0;")except RuntimeError: # If the column already exists, do nothing passKuzu is able to natively scan Pandas DataFrames in a zero-copy manner, allowing efficient data
transfer between the data in Python and Kuzu. The following code snippet shows how this is done for
the Movie nodes:
# Copy pagerank values to movie nodesx = conn.execute( """ LOAD FROM movie_df MERGE (m:Movie {movieId: id}) ON MATCH SET m.pagerank = pagerank RETURN m.movieId AS movieId, m.pagerank AS pagerank; """) movieId pagerank0 1 0.0007761 3 0.0002002 6 0.0003683 47 0.0007074 50 0.000724The same can be done for user nodes.
# Copy user pagerank values to user nodesy = conn.execute( """ LOAD FROM user_df MERGE (u:User {userId: id}) ON MATCH SET u.pagerank = pagerank RETURN u.userId AS userId, u.pagerank AS pagerank; """) userId pagerank0 1 0.0008671 2 0.0001342 3 0.0002543 4 0.0009294 5 0.000151Query PageRank values in Kuzu
You can now run a query to print the top 5 Movie nodes ordered by their PageRank values:
res1 = conn.execute( """ MATCH (m:Movie) RETURN m.title, m.pagerank ORDER BY m.pagerank DESC LIMIT 5; """)print(res1.get_as_df()) m.title m.pagerank0 Forrest Gump (1994) 0.0011551 Shawshank Redemption, The (1994) 0.0010992 Pulp Fiction (1994) 0.0010753 Matrix, The (1999) 0.0010064 Silence of the Lambs, The (1991) 0.000987And similarly, for the User nodes:
res2 = conn.execute( """ MATCH (u:User) RETURN u.userId, u.pagerank ORDER BY u.pagerank DESC LIMIT 5; """)print(res2.get_as_df()) u.userId u.pagerank0 599 0.0164011 414 0.0147112 474 0.0143803 448 0.0129424 610 0.008492Further work
You’ve now seen how to use NetworkX to run algorithms on a Kuzu graph and move data back and forth between Kuzu and Python.
There are numerous additional computations you can perform in NetworkX and store these results in Kuzu. See the tutorial notebook on Google Colab to try it for yourself!

