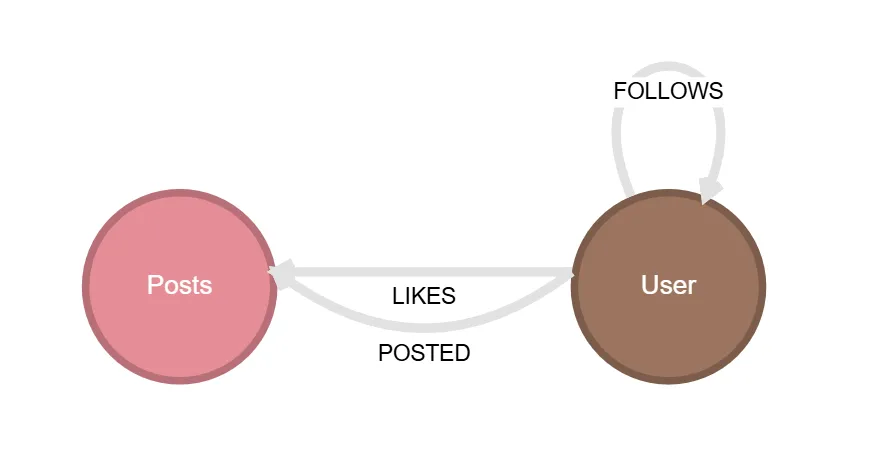
Example database
The dataset used in the tutorials is a social network dataset of users and posts that has the following schema.
Download the data
You can download the zipped data by clicking on this link, or use curl as shown below. Once downloaded, unzip the files to your current working directory.
curl -o tutorial_data.zip https://kuzudb.com/data/tutorial/tutorial_data.zipunzip tutorial_data.zipNodes
User
The User node represents users within the social network. Each user has their information attached, such as:
- user_id (INT64): This is a unique ID which is used to sort and find users.
- username (STRING): This is the unique username which each user will have.
- account_creation_date (DATE): This represents the date which the account was created.
userID,username,account_creation_date1,epicwolf202,2022-09-092,silentninja637,2023-01-273,stormcat597,2023-02-254,brightking765,2023-05-115,fastgirl798,2021-06-11Post
The Post node represents the posts which have been made on the social network. Each post has its information attached, such as:
- post_id (INT64): This is a unique ID which is used to sort and find posts.
- creation_date (DATE): This represents the date which the post was created.
- like_count (INT64): This represents the number of likes the post has received.
- retweet_count (INT64): This represents the number of retweets the post has received.
postID,creation_date,like_count,retweet_count1,2021-12-08,427,292,2022-06-02,9,163,2023-01-14,238,514,2023-01-06,67,1475,2022-10-26,103,73Relationships
FOLLOWS
The relationship FOLLOWS goes from User node to User node. This relation represents a user following another user on the social network.
followerID,followeeID1,71,62,172,102,13POSTS
The relationship POSTS goes from User node to Post node. This relation represents a user posting the post on the social network.
userID,postID17,14,215,37,414,5LIKES
The relationship LIKES goes from User node to Post node. This relation represents a user liking the post on the social network.
userID,postID16,12,14,113,111,1Create Kuzu tables
In the Kuzu CLI, let’s create a node table for the Users in our dataset.
// Create a node table for the `User`s in our dataset.CREATE NODE TABLE User( userID INT64 PRIMARY KEY, username STRING, account_creation_date DATE);
// Create a node table for the `Post`s in our dataset.CREATE NODE TABLE Post( postID INT64 PRIMARY KEY, creation_date DATE, like_count INT64, retweet_count INT64);
// Create a relationship table for the `FOLLOWS` relationship in our dataset.CREATE REL TABLE FOLLOWS(From User To User);
// Create a relationship table for the `POSTS` relationship in our dataset.CREATE REL TABLE POSTED(From User To Post);
// Create a relationship table for the `LIKES` relationship in our dataset.CREATE REL TABLE LIKES(From User To Post);This will create the required node and relationship tables in Kuzu.

